Customization
Identifying the need for a new machine and conceptualizing its design, including research, brainstorming, and creating initial sketches.
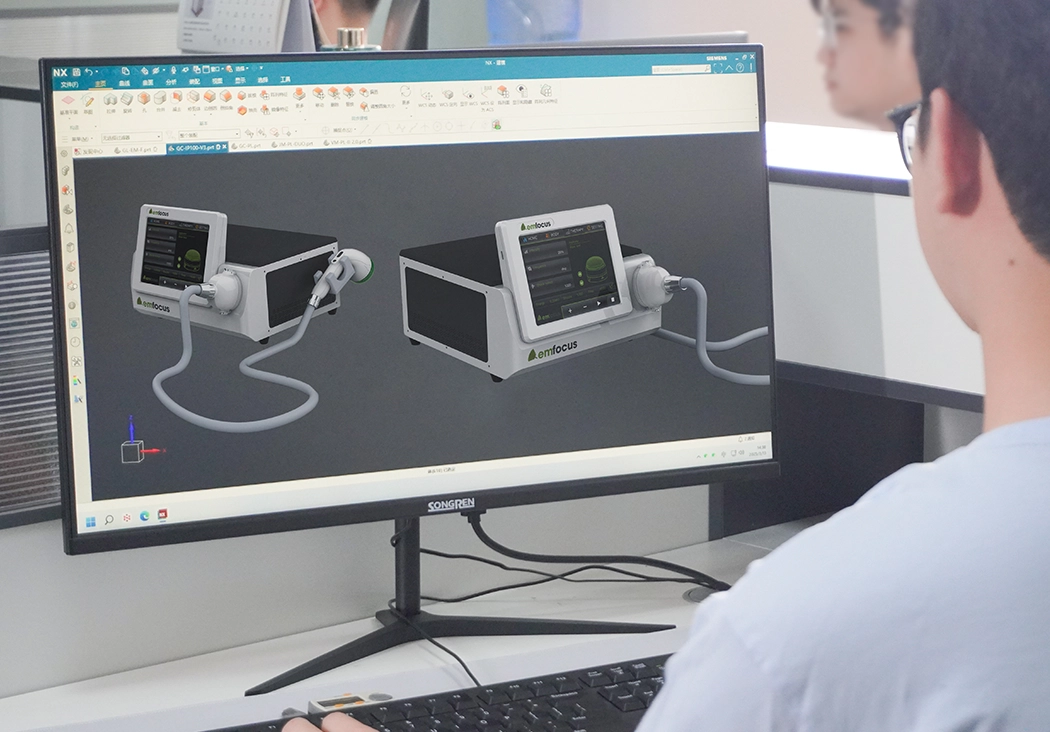
Prototype
Once the design is finalized, engineers and designers use CAD software to create detailed designs and specifications for the machine. A prototype is then built to test and refine the design.
Mechanical Engineering
After the prototype is approved, the necessary components and materials are sourced from suppliers. These include electronic components, motors, sensors, housing materials, cables, etc. The machine's various parts are then manufactured, either in-house or outsourced to specialized manufacturers.
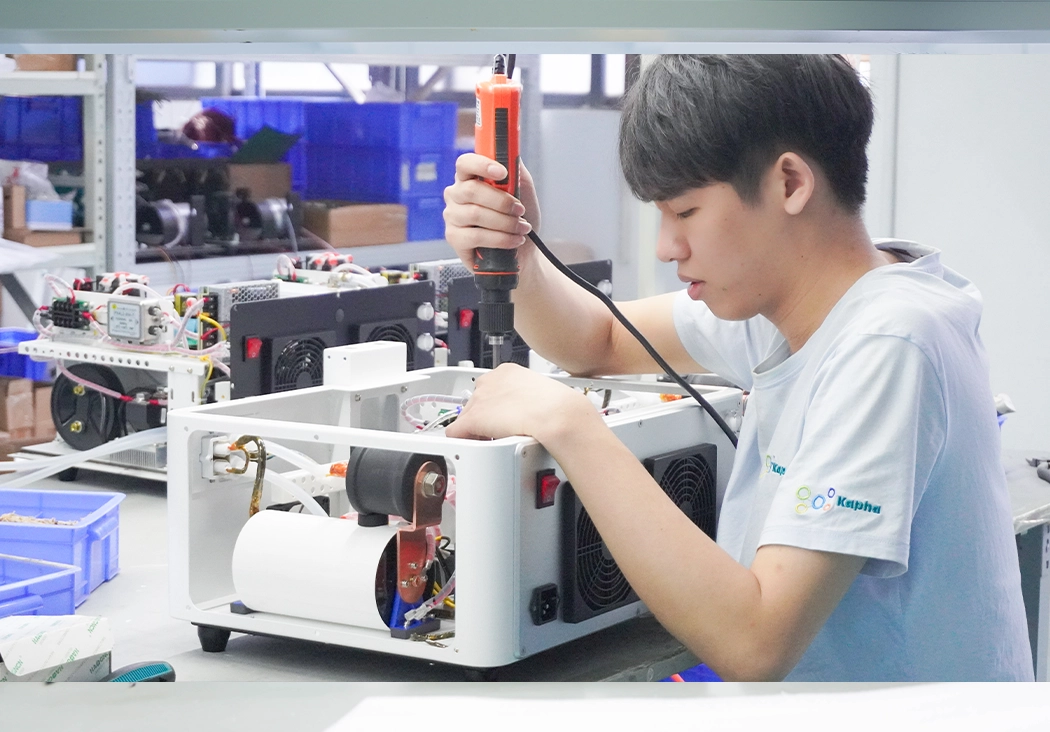
Product Assembling
The manufactured components are assembled together following the design specifications. This includes integrating the electronics, motors, sensors, mechanical parts, and any other necessary elements. Quality checks are performed at each stage to ensure proper assembly.
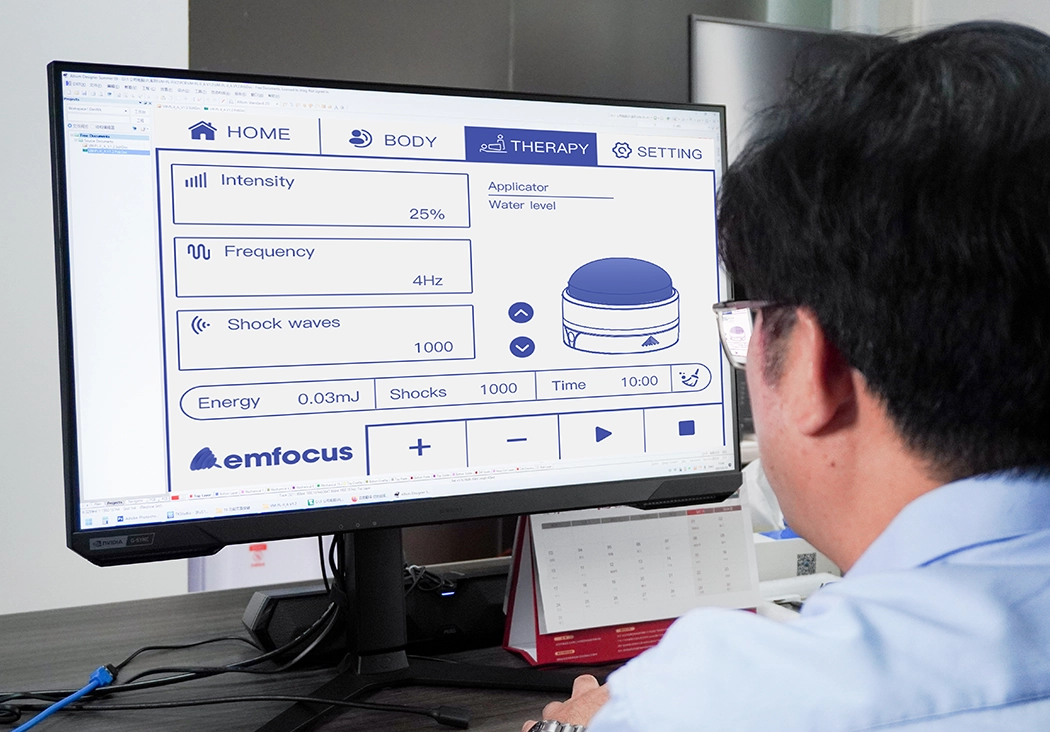
Software Customization
The software is developed and integrated into the machine. This involves programming the user interface, creating algorithms, calibration processes, and ensuring compatibility with other devices or systems.
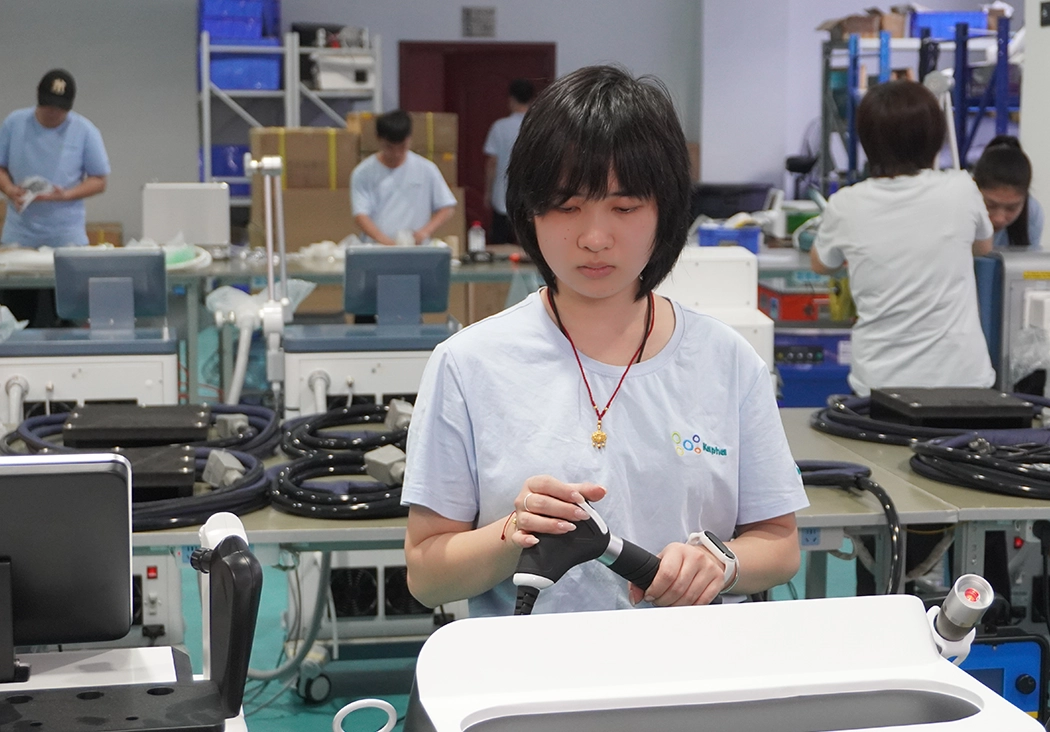
Quality Check
Once the machine is fully assembled and integrated, it undergoes extensive testing to ensure it functions correctly and safely. This includes functional tests, performance tests, electrical safety tests, and endurance tests. After successful testing, the machine can be certified for compliance with relevant safety and regulatory standards. Following certification, the machine can enter full-scale production for distribution and use.